Training a neural network for estimating the homeostatic model of insulin resistance
Main Article Content
Abstract
Introduction: the evaluation of the homeostatic model is a test very close to the gold standard (euglycemic clamp).
Objective: train a multilayer perceptron-type neural network to determine the homeostatic model of insulin resistance.
Methodology: analytical and cross-sectional study. The learning of the neural network was carried out from a database of 2004 Venezuelan adults. Subsequently, 4,363 Mexican adults were added to the database of the National Health and Nutrition Survey (ENSANUT). The variables were homeostatic model of insulin resistance (HOMA2-IR), basal insulin, and basal glucose. Multilayer perceptron-type neural networks were used.
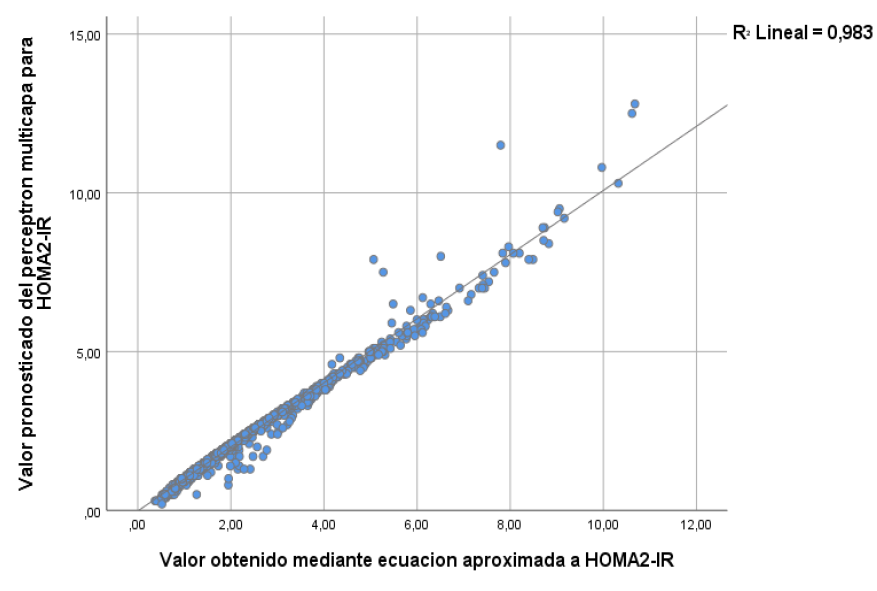
Results: the training of the neural network model had a relative error of 0.003, while in the test it was 0.005. For qualitative HOMA2-IR, the percentage of incorrect predictions was 0.60 % in training, and 0.70 % in testing. After learning the model, insulin and basal glucose values from 4363 Mexican adults were added, observing that the HOMA2-IR values generated by multilayer perceptron maintained the efficiency of the model, obtaining a coefficient of determination R2 of 0.983, which implies that 98 % of the variation in HOMA2-IR values can be explained by HOMA2-IR values obtained using multilayer perceptron.
Conclusions: the multilayer perceptron-type neural network gives results virtually identical to those obtained using the HOMA2-IR calculator. The implementation of this algorithm can be beneficial as a tool that is easy to implement in primary and specialized care systems and in hospital environments.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Usted es libre de:
- Compartir: copiar y redistribuir el material en cualquier medio o formato para cualquier propósito, incluso comercialmente.
- Adaptar: remezclar, transformar y construir a partir del material para cualquier propósito, incluso comercialmente.
- La licenciante no puede revocar estas libertades en tanto usted siga los términos de la licencia
Bajo los siguientes términos:
- Atribución: Usted debe dar crédito de manera adecuada, brindar un enlace a la licencia, e indicar si se han realizado cambios. Puede hacerlo en cualquier forma razonable, pero no de forma tal que sugiera que usted o su uso tienen el apoyo de la licenciante.
- Compartir igual: — Si remezcla, transforma o crea a partir del material, debe distribuir su contribución bajo la misma licencia del original.
- No hay restricciones adicionales — No puede aplicar términos legales ni medidas tecnológicas que restrinjan legalmente a otras a hacer cualquier uso permitido por la licencia.
References
Thota S, Akbar A. Insulin. [Updated 2023 Jul 10]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL):StatPearls Publishing; 2024
Freeman AM, Acevedo LA, Pennings N. Insulin Resistance. 2023 Aug 17. In: StatPearls [Internet].Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024
Ahmed B, Sultana R, Greene MW. Adipose tissue and insulin resistance in obese. BiomedPharmacother [Internet]. 2021;137(111315):111315. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111315
Almeda-Valdés P, Cuevas-Ramos D, Alberto Aguilar-Salinas C. Metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann Hepatol [Internet]. 2009;8(Supp 1):S18–24. doi: 10.1016/s1665-2681(19)31822-8
Kosmas CE, Bousvarou MD, Kostara CE, Papakonstantinou EJ, Salamou E, Guzman E. Insulinresistance and cardiovascular disease. J Int Med Res [Internet]. 2023;51(3):030006052311645. doi: 10.1177/03000605231164548
Szablewski L. Insulin resistance: the increased risk of cancers. Curr Oncol [Internet].2024;31(2):998–1027. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31020075
Gastaldelli A. Measuring and estimating insulin resistance in clinical and research settings. Obesity(Silver Spring). 2022;30(8):1549–63. doi: 10.1002/oby.23503
Muniyappa R, Madan R, Varghese RT. Assessing insulin sensitivity and resistance in humans[Internet]. MDText.com; 2021 [citado 30 de agosto de 2024]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278954/
Tahapary DL, Pratisthita LB, Fitri NA, Marcella C, Wafa S, Kurniawan F, et al. Challenges in thediagnosis of insulin resistance: Focusing on the role of HOMA-IR and Tryglyceride/glucose index. Diabetes Metab Syndr [Internet]. 2022;16(8):102581. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102581
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasismodel assessment: insulin resistance and ?-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia [Internet]. 1985;28(7):412–9. doi: 10.1007/bf00280883
Fan B, Wu H, Shi M, Yang A, Lau ESH, Tam CHT, et al. Associations of the HOMA2‐%B andHOMA2‐IR with progression to diabetes and glycaemic deterioration in young and middle‐aged Chinese. Diabetes Metab Res Rev [Internet]. 2022;38(5):412-419. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3525
Salazar J, Bermúdez V, Calvo M, Olivar LC, Luzardo E, Navarro C, et al. Optimal cutoff for theevaluation of insulin resistance through triglyceride-glucose index: a cross-sectional study in a Venezuelan population. F1000Res [Internet]. 2018;6:1337. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.12170.3
Bermúdez V, Rojas J, Martínez MS, Apruzzese V, Chávez-Castillo M, Gonzalez R, et al.Epidemiologic behavior and estimation of an optimal Cut-Off point for Homeostasis Model Assessment-2 Insulin Resistance: a report from a Venezuelan population. Int Sch Res Notices [Internet]. 2014;2014:1–10. doi: 10.1155/2014/616271
Bhattacharya S, Bennet L, Davidson JO, Unsworth CP. Multi-layer perceptron classification &quantification of neuronal survival in hypoxic-ischemic brain image slices using a novel gradient direction, grey level co-occurrence matrix image training. PLoS One [Internet]. 2022;17(12):e0278874. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278874
Chai SS, Cheah WL, Goh KL, Chang YHR, Sim KY, Chin KO. A multilayer perceptron neuralnetwork model to classify hypertension in adolescents using anthropometric measurements: A cross-sectional study in Sarawak, Malaysia. Comput Math Methods Med [Internet]. 2021;2021:1–11. doi: 10.1155/2021/2794888
Hamilton DF, Ghert M, Simpson AHRW. Interpreting regression models in clinical outcomestudies. Bone Joint Res. 2015;4(9):152–3. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.49.2000571
González-Martín JM, Torres-Mata LB, Cazorla-Rivero S, Fernández-Santana C, Gómez-Bentolila E, Clavo B, et al. An artificial intelligence prediction model of insulin sensitivity, insulin resistance, and diabetes using genes obtained through differential expression. Genes (Basel) [Internet]. 2023;14(12):2119. doi: 10.3390/genes14122119
Park S, Kim C, Wu X. Development and validation of an insulin resistance predicting model usinga machine-learning approach in a population-based cohort in Korea. Diagnostics (Basel) [Internet]. 2022 [citado 30 de agosto de 2024];12(1):212. Disponible en: https://www.mdpi.com/2075-4418/12/1/212
Chakradar M, Aggarwal A, Cheng X, Rani A, Kumar M, Shankar A. A non-invasive approach toidentify insulin resistance with triglycerides and HDL-c ratio using machine learning. Neural Process Lett [Internet]. 2023;55(1):93–113. doi: 10.1007/s11063-021-10461-6
Tsai S-F, Yang C-T, Liu W-J, Lee C-L. Development and validation of an insulin resistancemodel for a population without diabetes mellitus and its clinical implication: a prospective cohort study. EClinicalMedicine [Internet]. 2023;58(101934):101934. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101934