Neurophobia in Medical Students from Paraguay
Main Article Content
Abstract
Introduction: neurophobia, defined as the fear or aversion to neurology due to its perceived complexity, poses a challenge in medical education. This study examines the prevalence and associated factors of neurophobia among medical students in Paraguay.
Objective: to explore perceptions, attitudes, and factors associated with neurophobia among medical students and identify educational strategies to enhance neurology teaching.
Methodology: this was an observational, descriptive, and cross-sectional study conducted with a sample of 413 medical students from various Paraguayan universities. Data on sociodemographic characteristics, prior experiences in neurology, and knowledge perceptions were collected using a validated questionnaire. Descriptive and inferential statistical analyses were performed.
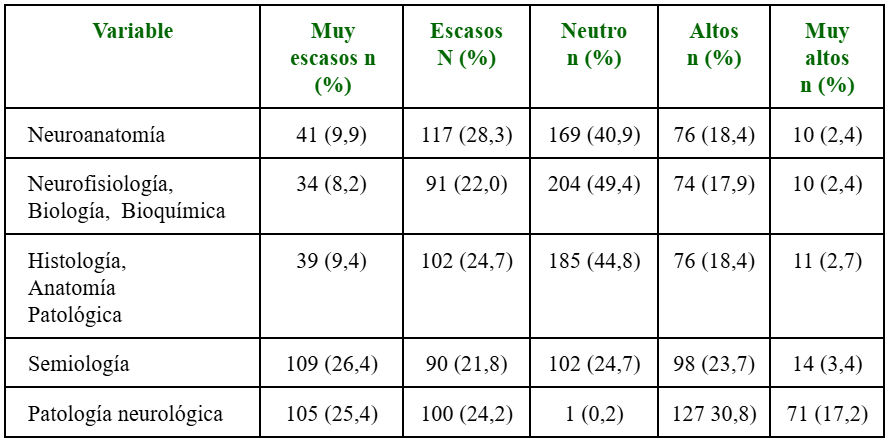
Results: a total of 41.6 % of students reported a low likelihood of choosing neurology as a specialty, while 33.9 % expressed intermediate levels of fear toward this discipline. The main causes of neurophobia were theoretical teaching approaches (32.9 %) and the perceived difficulty of neuroanatomy (35.8 %). Additionally, 69.2 % considered neurology teaching to be insufficient, and 81.1 % reported a lack of extracurricular activities related to neurology.
Conclusions: the findings highlight the need for a more practical and interactive curriculum, emphasizing clinical simulations and extracurricular activities to foster interest and confidence in neurology. These changes could mitigate neurophobia and encourage professional development in this specialty.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Usted es libre de:
- Compartir: copiar y redistribuir el material en cualquier medio o formato para cualquier propósito, incluso comercialmente.
- Adaptar: remezclar, transformar y construir a partir del material para cualquier propósito, incluso comercialmente.
- La licenciante no puede revocar estas libertades en tanto usted siga los términos de la licencia
Bajo los siguientes términos:
- Atribución: Usted debe dar crédito de manera adecuada, brindar un enlace a la licencia, e indicar si se han realizado cambios. Puede hacerlo en cualquier forma razonable, pero no de forma tal que sugiera que usted o su uso tienen el apoyo de la licenciante.
- Compartir igual: — Si remezcla, transforma o crea a partir del material, debe distribuir su contribución bajo la misma licencia del original.
- No hay restricciones adicionales — No puede aplicar términos legales ni medidas tecnológicas que restrinjan legalmente a otras a hacer cualquier uso permitido por la licencia.
References
Jozefowicz RF. Neurophobia: the fear of neurology among medical students. Arch Neurol. 1994;51(4):328-9. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1994.00540160018003.
Hernández A, Pedersoli LC, Pedersoli M. Neurofobia en el estudiante de medicina: aplicación de historia clínica virtual como herramienta evaluativa. Tercera Época. 2017;7(1):1-1.
Díaz L, Velásquez J, Pérez G. Neurofobia: frecuencia y descripción de factores relacionados en una universidad Latinoamericana en 2019. Neurología Argentina. 2020;12(4):239-246. doi: 10.1016/j.neuarg.2020.07.007.
Schon F, Hart P, Fernandez C. Is clinical neurology really so difficult? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002;72(5):557-9. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.72.5.557.
Moreno-Zambrano D, Sandrone S, Meza-Venegas J, Jimenez J, Freire-Bonifacini A, Santibanez-Vasquez R, et al. Exploring the key factors behind neurophobia:a systematic review of the English, Spanish and Portuguese literature. Brain Disord. 2021;2:100011. doi: 10.1016/j.dscb.2021.100011.
Lambea-Gil Á, Saldaña-Inda I, Lamíquiz-Moneo I, Cisneros-Gimeno AI. Neurofobia entre los estudiantes de medicina de una universidad española: experiencias más allá de la anglosfera. Rev Neurol. 2023;76(11):351–359. doi: 10.33588/rn.7611.2023102.
McCarron MO, Stevenson M, Loftus AM, McKeown P. Neurophobia among general practice trainees: the evidence, perceived causes and solutions. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2014;122:124-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2014.03.021.
Restrepo J, Aldana R, Álvarez JC, Botero Díaz LC, Durán Barrera MC, Espinel Laverde BF, et al. Percepción de neurofobia en estudiantes del último año de Medicina en una universidad privada. Acta Neurol Colomb. 2017;33(2):63-67. doi: 10.22379/24224022135.
Morínigo D, Fleitas D, Morel Pirelli M, Velázquez G. Neurofobia en estudiantes de postgrado en Medicina Interna. Rev. virtual Soc. Parag. Med. Int. 2017;4(2):42-48. doi: 10.18004/rvspmi/2312-3893/2017.04(02)42-048.
Organización Mundial de la Salud. Más de 1 de cada 3 tienen afecciones neurológicas, la principal causa de enfermedad y discapacidad en todo el mundo [Internet]. OMS: Ginebra; 2024 [consultado 15 Noviembre, 2024]. Disponible en: https://www.who.int/es/news/item/14-03-2024-over-1-in-3-people-affected-by-neurological-conditions--the-leading-cause-of-illness-and-disability-worldwide
GBD 2021 Nervous System Disorders Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of disorders affecting the nervous system, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Neurol. 2024;23(4):344-381. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(24)00038-3. Erratum in: Lancet Neurol. 2024 May;23(5):e9. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(24)00114-5. Erratum in: Lancet Neurol. 2024;23(7):e11. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(24)00231-X.
Torales J, Barrios I. Diseño de investigaciones: algoritmo de clasificación y características esenciales. Med. clín. soc. 2023;7(3):210-235. doi: 10.52379/mcs.v7i3.349.
Muñoz Navarro SR. ¿Cuántos sujetos necesito para mi estudio?. Medwave. 2014;14(6):e5995. doi: 10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5995.
Yang Y, Li J, Wu X, Wang J, Li W, Zhu Y, et al. Factors influencing subspecialty choice among medical students: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2019;9(3):e022097. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-022097.
Levaillant M, Levaillant L, Lerolle N, Vallet B, Hamel-Broza JF. Factors influencing medical students' choice of specialization: A gender based systematic review. E Clinical Medicine. 2020;28:100589. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100589.
Hernando-Requejo V. Neurophobia: why, how much, consequences and solutions. Med Ed Publish (2016). 2020;9:3. doi: 10.15694/mep.2020.000003.1.
Pfarrwaller E, Maisonneuve H, Laurent C, Abbiati M, Sommer J, Baroffio A, et al. Dynamics of students' career choice: a conceptual framework-based qualitative analysis focusing on primary care. J Gen Intern Med. 2024;39(9):1544-1555. doi: 10.1007/s11606-023-08567-9.
Anderson R, Bury M. Living with Chronic Illness: The experience of patients and their families. London: Taylor & Francis; 2024.
Ammann-Schnell L, Groeschel S, Kehrer C, Frölich S, Krägeloh-Mann I. The impact of severe rare chronic neurological disease in childhood on the quality of life of families-a study on MLD and PCH2. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021;16(1):211. doi: 10.1186/s13023-021-01828-y.
Jukna Š, Puteikis K, Mameniškienė R. Perception of neurology among undergraduate medical students - what can be done to counter neurophobia during clinical studies? BMC Med Educ. 2023;23(1):447. doi: 10.1186/s12909-023-04405-y.
Sandrone S, Carlson C. Gamification and game-based education in neurology and neuroscience: Applications, challenges, and opportunities. Brain Disord.2021;1:100008. doi: 10.1016/j.dscb.2021.100008.
Tuma F. The use of educational technology for interactive teaching in lectures. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021;62:231-235. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2021.01.051.
Sandrone S, Berthaud JV, Carlson C, Cios J, Dixit N, Farheen A, et al. Strategic considerations for applying the flipped classroom to neurology education. Ann Neurol. 2020;87(1):4-9. doi: 10.1002/ana.25609.
Kaygısız Ç. Educational neuroscience: issues and challanges. Erciyes Journal of Education. 2022;6(1): 80-98. doi: 10.32433/eje.990407.
Han F, Zhang Y, Wang P, Wu D, Zhou LX, Ni J. Neurophobia among medical students and resident trainees in a tertiary comprehensive hospital in China. BMC Med Educ. 2023;23(1):824. doi: 10.1186/s12909-023-04812-1.
Adel A. Exploring resistance in the context of social justice education in undergraduate medical education (Master's thesis). University of Calgary; 2024. Disponible en: https://hdl.handle.net/1880/118991
Hull W, Jewell E, Shabir S, Borrows R. Nephrophobia: a retrospective study of medical students' attitudes towards nephrology education. BMC Med Educ. 2022;22(1):667. doi: 10.1186/s12909-022-03713-z.
Mergen M, Meyerheim M, Graf N. Reviewing the current state of virtual reality integration in medical education - a scoping review protocol. Syst Rev. 2023;12(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s13643-023-02266-6.
Roy S, Meena T, Lim SJ. Demystifying supervised learning in healthcare 4.0: a new reality of transforming diagnostic medicine. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022;12(10):2549. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12102549
Almousa O, Zhang R, Dimma M, Yao J, Allen A, Chen L, et al. Virtual reality technology and remote digital application for tele-simulation and global medical education: an innovative hybrid system for clinical training. simul gaming. 2021; 52(5):614-634. doi: 10.1177/10468781211008258.
Bramley AL, McKenna L. Entrustable professional activities in entry-level health professional education: a scoping review. Med Educ. 2021;55(9):1011-1032. doi: 10.1111/medu.14539.32.
Bodolica V, Spraggon M, Badi H. Extracurricular activities and social entrepreneurial leadership of graduating youth in universities from the Middle East. Int J Manag Educ. 2021;19(2):100489. doi: 10.1016/j.ijme.2021.100489.
Trinh LN, O'Rorke E, Mulcahey MK. Factors influencing female medical students' decision to pursue surgical specialties: a systematic review. J Surg Educ. 2021;78(3):836-849. doi: 10.1016/j.jsurg.2020.08.050.