Enterotoxins in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from food handlers at a public market in Asunción, Paraguay
Main Article Content
Abstract
Introduction: Staphylococcal food poisoning (SFA) is the most common foodborne toxin-borne illness in the world, but it is not a notifiable disease. Therefore, surveillance of Staphylococcus aureus carriage in food handlers is essential for outbreak prevention.
Objective: to detect enterotoxin-coding genes in S. aureus isolates collected from the nasal mucosa of food handlers from a public market in Asuncion, Paraguay in October 2023.
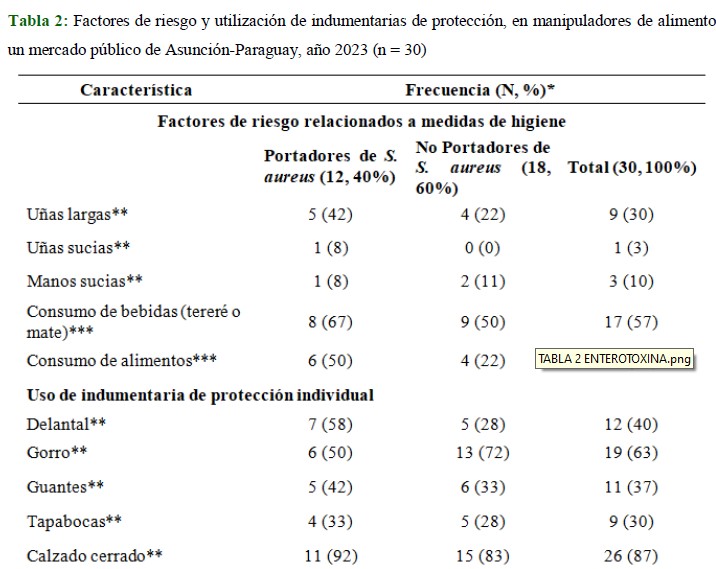
Methodology: descriptive observational design, cross-sectional, pilot project. Nasal swab samples were taken from 30 food handlers and cultured on blood agar and salted mannitol, the strains were identified by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry technique. Detection of enterotoxin A, B, C, D, G, H, I, M, N, O and U genes was performed by PCR.
Results: we found a high prevalence of nasal carriage of S. aureus (40 %, 12/30) in food handlers of a public market in Asunción, with 50 % (6/12) carrying the enterotoxin M gene and other genes in smaller proportion: G, I, O, U (17 %, 2/12) and C (8 %, 1/12).
Conclusion: we report the asymptomatic nasal carriage of S. aureus carrying enterotoxins by food handlers in a public market in Asunción, whose importance lies in the severity of the clinical pictures that could be caused by the single expression of any of these virulence factors in the event of a food outbreak.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Usted es libre de:
- Compartir: copiar y redistribuir el material en cualquier medio o formato para cualquier propósito, incluso comercialmente.
- Adaptar: remezclar, transformar y construir a partir del material para cualquier propósito, incluso comercialmente.
- La licenciante no puede revocar estas libertades en tanto usted siga los términos de la licencia
Bajo los siguientes términos:
- Atribución: Usted debe dar crédito de manera adecuada, brindar un enlace a la licencia, e indicar si se han realizado cambios. Puede hacerlo en cualquier forma razonable, pero no de forma tal que sugiera que usted o su uso tienen el apoyo de la licenciante.
- Compartir igual: — Si remezcla, transforma o crea a partir del material, debe distribuir su contribución bajo la misma licencia del original.
- No hay restricciones adicionales — No puede aplicar términos legales ni medidas tecnológicas que restrinjan legalmente a otras a hacer cualquier uso permitido por la licencia.
References
Ikuta KS, Swetschinski LR, Aguilar GR, Sharara F, Mestrovic T, Gray AP, et al. Global mortality associated with 33 bacterial pathogens in 2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. The Lancet [Internet]. 2022;400(10369):2221–48. Disponible en: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(22)02185-7/fulltext.
Authority (EFSA) EFS, European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The European Union One Health 2022 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J [Internet]. 2023;21(12):e8442. Disponible en: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.2903/j.efsa.2023.8442
Almeida A de, Aranda EFM, Chow CT, Ribeiro T, Veronese AGAP, Rivas JJDZ. Portación nasal de staphylococcus aureus en trabajadores de la salud del Hospital Distrital de Presidente Franco, 2020. Rev Científica Estud E Investig [Internet]. 2022;11(1):85–97. Disponible en: https://revista.unibe.edu.py/index.php/rcei/article/view/659
Zhu Z, Hu Z, Li S, Fang R, Ono HK, Hu DL. Molecular characteristics and pathogenicity of staphylococcus aureus exotoxins. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;25(1):395.
Manfredi EA, Leotta GA, Rivas M. PCR múltiple para la detección de los genes sea, seb, sec, sed y see de Staphylococcus aureus: Caracterización de aislamientos de origen alimentario. Rev Argent Microbiol [Internet]. 2010;42(3):212–5. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.ar/scielo.php?script=sci_abstract&pid=S0325-75412010000300013&lng=es&nrm=iso&tlng=es
Ghoreyshizadeh E, Manouchehrifar M, Ramazanzadeh R, PeeriDoghaheh H, Amani M, Arzanlou M. Occurrence and characteristics of toxigenic Staphylococcus aureus in retail foods in Iran. Food borne Pathog Dis. 2024;21(5):331–8.
Salina M, Scholz L, Servián N, Romero M, Samudio T, Ruiz V, et al. Portación de Staphylococcus Aureus en manipuladores de alimentos de servicios gastronómicos de Asunción, Paraguay (2017). Rev Salud Publica Parag [Internet]. 2018;8(2):28–33. Disponible en: http://scielo.iics.una.py/scielo.php?script=sci_abstract&pid=S2307-33492018000200028&lng=en&nrm=iso&tlng=es
Alarcón-Lavín MP, Oyarzo C, Escudero C, Cerda-Leal F, Valenzuela FJ, Alarcón-Lavín MP, et al. Portación de Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxigénico tipo A, en frotis nasofaríngeos en manipuladores de alimentos. Rev Médica Chile [Internet]. 2017;145(12):1559–64. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.cl/scielo.php?script=sci_abstract&pid=S0034-98872017001201559&lng=es&nrm=iso&tlng=es
Toribio Jiménez J, Ojendiz Mata YC, Orbe Díaz D, López-Damián LJ, Pérez Salgado J, Forero Forero AV, et al. Portadores asintomáticos de Staphylococcus aureus meticilino resistentes (MRSA) en pescadores y horticultores de Guerrero, México. J Negat No Posit Results JONNPR [Internet]. 2020;5(12):1482–9. Disponible en: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=780279
Fisher EL, Otto M, Cheung GYC. Basis of virulence in enterotoxin-mediated staphylococcal food poisoning. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:436.
Abril A, Villa T, Barros-Velázquez J, Cañas B, Sánchez-Pérez A, Calo-Mata P, et al. Staphylococcus aureus exotoxins and their detection in the dairy industry and mastitis. Toxins [Internet]. 2020;12(9):537. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7551672/
Hennekinne JA, Ostyn A, Guillier F, Herbin S, Prufer AL, Dragacci S. How should staphylococcal food poisoning outbreaks be characterized? Toxins [Internet]. 2010;2(8):2106–16. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3153283/
Nagaraj S, Ramlal S, Kingston J, Batra HV. Development of IgY based sandwich ELISA for the detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin G (SEG), an egc toxin. Int J FoodMicrobiol. 2016;237:136–41.
Cieza MYR, Bonsaglia ECR, Rall VLM, dos Santos MV, Silva NCC. Staphylococcal Enterotoxins: description and Importance in Food. Pathogens [Internet]. 2024;13(8):676. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11357529/
Fries BC, Varshney AK. Bacterial Toxins—Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B. MicrobiolSpectr [Internet]. doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.AID-0002–2012.
Grispoldi L, Karama M, Armani A, Hadjicharalambous C, Cenci-Goga BT. Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin in food of animal origin and staphylococcal food poisoning risk assessment from farm to table. Ital J AnimSci [Internet]. 2021;20(1):677–90. Disponible en: https://doi.org/10.1080/1828051X.2020.1871428
Weiler N, Leotta GA, Zárate MN, Manfredi E, Álvarez ME, Rivas M. Brote de intoxicación alimentaria asociado al consumo de leche ultrapasteurizada en la República del Paraguay. Rev Argent Microbiol [Internet]. 2011;43(1):33–6. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.ar/scielo.php?script=sci_abstract&pid=S0325-75412011000100007&lng=es&nrm=iso&tlng=es
Rodríguez-Acosta F, Carpinelli L, Basualdo W, Castro H, Quiñonez B, Argüello R, et al. Frecuencia de genes que codifican factores de virulencia en Staphylococcus aureus aislados de niños que concurrieron al Hospital General Pediátrico Niños de Acosta Ñú, durante el año 2010. Mem InstInvestig en Cienc Salud [Internet]. 2015;13(1). Disponible en: https://revistascientificas.una.py/index.php/RIIC/article/view/1796
Guillén R, Salinas C, Mendoza-Álvarez A, Rubio Rodríguez LA, Díaz-de Usera A, Lorenzo-Salazar JM, et al. Genomic epidemiology of the primary methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones causing invasive infections in Paraguayan children. Microbiol Spectr [Internet]. 2024;12(4):e03012-23. Disponible en: https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/spectrum.03012-23
Koneman EW. Koneman’s color atlas and textbook of diagnostic microbiology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006. 1784 p.
Herman-Bausier P, Labate C, Towell AM, Derclaye S, Geoghegan JA, Dufrêne YF. Staphylococcus aureus clumping factor A is a force-sensitive molecular switch that activates bacterial adhesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(21):5564–9.
Jarraud S, Peyrat MA, Lim A, Tristan A, Bes M, Mougel C, et al. Egc, a highly prevalent operon of enterotoxin gene, forms a putative nursery of superantigens in Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol Baltim Md 1950. 2001;166(1):669–77.
Wu D, Li X, Yang Y, Zheng Y, Wang C, Deng L, et al. Superantigen gene profiles and presence of exfoliative toxin genes in community-acquired meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from Chinese children. J Med Microbiol. 2011;60(Pt 1):35–45.
Fooladvand S, Sarmadian H, Habibi D, van Belkum A, Ghaznavi-Rad E. High prevalence of methicillin resistant and enterotoxin gene-positive Staphylococcus aureus among nasally colonized food handlers in central Iran. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis Off Publ Eur SocClin Microbiol. 2019;38(1):87–92.
Jeanette AFF Cabral P Leilah Graciela, Walde L. Portación nasal de Staphylococcus aureus en manipuladores de alimentos del Mercado No 4 de Asunción, Paraguay. Rev ANACEM. 20212:6(1):14. Disponible en: https://www.imbiomed.com.mx/articulo.php?id=83175
Di Gregorio S, Vielma J, Haim MS, Rago L, Campos J, Kekre M, et al. Genomic epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bloodstream infections in South America during 2019 supports regional surveillance. Microb Genomics [Internet]. 2023;9(5):mgen001020. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10272885/
Guillén R, Carpinelli L, Rodríguez F, Castro H, Quíñónez B, Campuzano A, et al. Staphylococcus aureus adquiridos en la comunidad: caracterización clínica, fenotípica y genotípica de aislados en niños paraguayos. Rev Chil Infectol [Internet]. 2016;33(6):609–18. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.cl/scielo.php?script=sci_abstract&pid=S0716-10182016000600002&lng=es&nrm=iso&tlng=es
Zhao Y, Tang J, Yang D, Tang C, Chen J. Corrigendum to “Staphylococcal enterotoxin M induced inflammation and impairment of bovine mammary epithelial cells” (J. Dairy Sci. 103:8350–8359). J Dairy Sci [Internet]. 2022;105(8):7140. Disponible en: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S002203022200385X
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Cai R, Shi L, Li C, Yan H. Prevalence of Enterotoxin Genes in Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Pork Production. Food borne Pathog Dis [Internet]. 2018;15(7):437–43. Disponible en: http://www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/fpd.2017.2408
Labrecque S, Shah S, Fergus D, Parry MF. Mupirocin susceptibility of staphylococci 2022: is it time for a change in MRSA decolonization protocols? Am J Infect Control [Internet]. 2023;51(7):725–8. Disponible en: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0196655322006575